2535441 No abstract available. A non-gapped metabolic acidosis fall into three categories.

Pin On R1 Common Medical Emergency
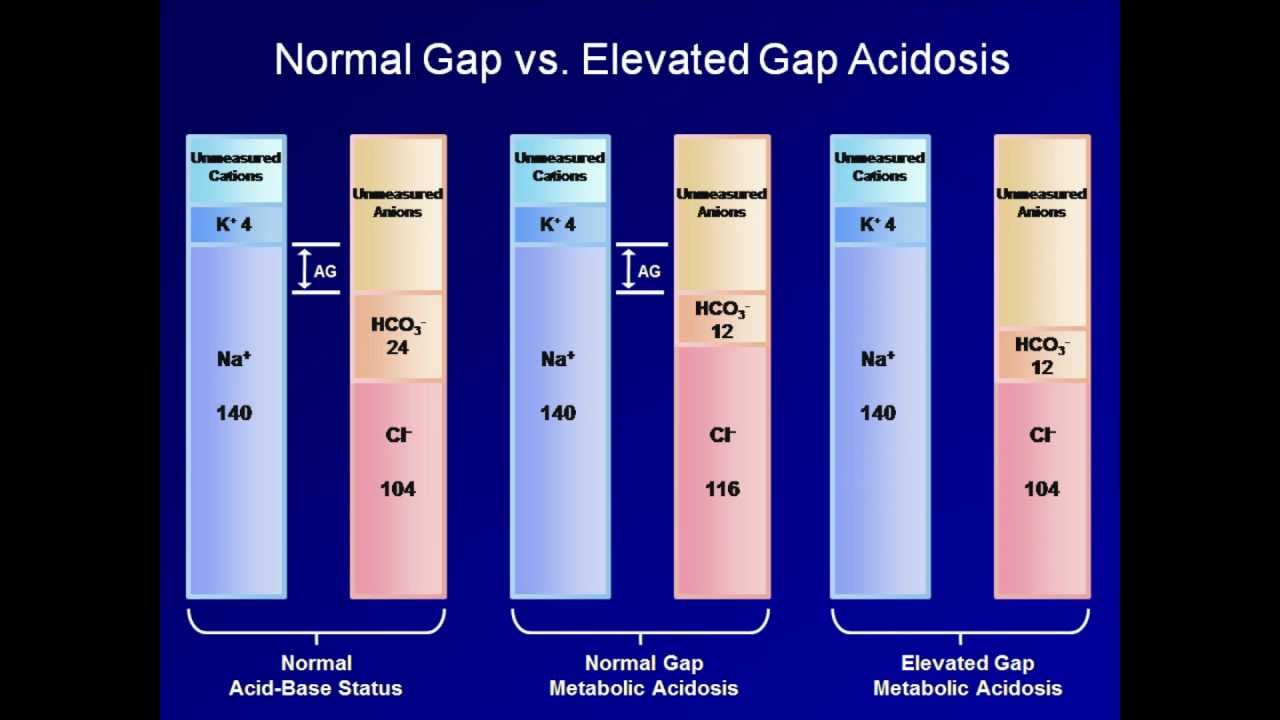
Anion gap Na - Cl- - HCO3- or alternative formula.

. A normal value is usually 3-16 but may vary slightly depending on the technique used by the local laboratory. Normal anion gap metabolic acidosis is a common but often misdiagnosed clinical condition associated with diarrhea and renal tubular acidosis RTA. Its urinary rate of excretion UNH4 may be increased several fold in the presence of extrarenal metabolic acidosis.
The anion gap can be used to help identify the cause of metabolic acidosis. The value of the anion gap is reported in milliequivalents per liter mEqL. Metabolic acidosis can be caused by acid accumulation due to increased acid production or acid ingestion.
Normal anion gap acidosis results from either bicarbonate dilution secondary to fluid resuscitation with 09 sodium chloride or abnormal bicarbonate loss from the gut or the kidneys renal tubular acidosis. The two major causes of hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis are HCO 3 loss from the GI tract or defects in renal acidification RTA Table 2112 and Table 2114. A step-by-step approach to a clinical case Clin Invest Med.
Normal values are 3 to 11 mEqL 4 2. Author P Vinay 1 Affiliation 1 Nephrology Service Hôpital Notre-Dame Montréal Québec. The most important treatment of anion-gap metabolic acidosis is the reversal of its cause.
Because the anion gap is greater than 12 its abnormally high. Some older types of tests used different techniques to measure electrolytes which give different results. Normal anion gap readings range from 310 milliequivalents per liter.
Healthcare providers most commonly use anion gap to identify cases of metabolic acidosis when you have higher-than-normal amounts of acid in your blood. Other causes of metabolic acidosis eg renal tubular acidosis may have a normal anion gap. Is 5 a low anion gap.
Or GI or renal bicarbonate HCO 3 loss. What is non anion gap metabolic acidosis. Please define the Anion Gap and its utility in diagnosis and how it relates to osmolality.
If the anion gap is. The urinary anion gap can help differentiate between these causes. A normal value is usually 3-16 but may vary slightly depending on the technique used by the local laboratory.
Anion gap metabolic acidosis is metabolic acidosis characterized by a buffering of nonchloride acids resulting in decreased serum pH and bicarbonate without an elevation in serum chloride increased anion gap as calculated from Na - Cl- HCO 3. CO2 assess if respiratory compensation is appropriate. 8 to 16 if measured by older technique of flame photometry.
Primary respiratory acidosis if pCO2 pCO2expected. 8 to 16 meqL. Hypoalbuminemia is the most common cause of a low anion gap.
Early identification of RTA remains challenging for inexperienced physicians and. Uremic AGMA Traditionally bicarbonate has been used to support the pH in efforts to stave off dialysis. An anion gap blood test checks the acid-base balance of your blood and if the electrolytes in your blood are properly balanced.
This will vary depending on the etiology. The compensatory increase in serum chloride hyperchloremia maintains electroneutrality and a normal anion gap. Normal Anion Gap 12-4 8-16 12-20 mEqL when including K.
Elevated anion gap can also be seen in presence of other mixed acid-base disorders with or without a change in blood pH 2. Ammonium is a major urinary buffer that is necessary for the normal excretion of the daily acid load. Because UNH4 is not commonly measured in clinical.
Readings outside this range may indicate a pH imbalance and this can stem from a wide variety. Normal Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis NAGMA HCO3 loss and replaced with Cl- - anion gap normal. The goal here is to mimic the normal physiology of compensatory respiratory alkalosis a.
The excessive loss of bicarbonate results in a low plasma bicarbonate concentration which ends up lowering the ph in response the kidneys start reabsorbing more chloride ions so for each bicarbonate ion thats lost theres a new chloride ion this is why normal anion gap metabolic acidosis is sometimes called a hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Normal anion gap acidosis is caused by carbonic anhydrase inhibitors hydrochloride salts of amino acids toluene amphotericin spironolactone and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugsThe mechanism by which these substances produce metabolic acidosis and the. The normal anion gap is 12.
From TPN containing ammonium chloride Acetazolamide and other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. Therefore values greater than 12 define an anion gap metabolic acidosis. Lab Appointments Locations.
There are usually more measurable cations than anions and thus a normal anion gap is value is positive. Always determine if there is another acidbase process occurring. Primary acidosis if pH.
Therefore measurement of UNH4 can provide important clues about causes of metabolic acidosis. Hyperalimentation eg. Non-gap metabolic acidosis or hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis are a group of disorders characterized by a low bicarbonate hyperchloremia and a normal anion gap 10-12.
With a normal anion gap metabolic acidosis the reduction in bicarbonate is mirrored by an increase in chloride concentration. Primary respiratory alkalosis if pCO2 pCO2expected. AG Na K - Cl- - HCO3-.
Respiratory compensation is the physiologic mechanism to help normalize a metabolic acidosis however compensation never completely corrects an acidemia. If the anion gap is. The normal anion gap depends on serum phosphate and serum albumin concentrations An elevated anion gap strongly suggests the presence of a metabolic acidosis The normal anion gap varies with different assays but is typically 4 to 12mmolL if measured by ion selective electrode.
Metabolic acidoses are categorized based on whether the anion gap is high or normal. Metabolic acidosis with normal anion-gap. Metabolic acidosis associated with a normal anion gap can occur from the loss of bicarbonate and the retention of the chloride ion hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis.
If hyponatraemia is present the plasma Cl- may be normal despite the presence of a normal anion gap acidosis - this could be considered a relative hyperchloraemia. There are usually more measurable cations than anions and thus a normal anion gap is value is positive. Anion Gap Blood Test.
1 loss of base bicarbonate from the gastrointestinal GI tract or. The differential diagnosis of normal anion gap acidosis is relatively short when compared to the differential diagnosis of acidosis.

Pin By Vijay Nath On Medicine Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Acidosis

Rosh Review Metabolic Acidosis Acidosis And Alkalosis Emt Study

The Classic Mnemonic Often Used To Remember The Causes Of Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Is Mudpiles M Metha Medical Mnemonics Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis

Questions Asked By A Student At Sgd Why In Metabolic Acidosis The Compensation Has No Acute Phase Why Acidosis Metabolic Acidosis Respiratory Alkalosis

Pin By Miroslawa Bodnar On Pa Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Normal Values

Pin On Anemia And Renal Nutrition

Dx Schema Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis The Clinical Problem Solvers Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Acidosis

Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Emcrit Project Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Acidosis And Alkalosis

Respiratory Alkalosis Metabolic Acidosis Metabolic Alkalosis

Metabolic Acidosis Metabolic Acidosis Acidosis Anion Gap

Renal Tubular Acidosis Is An Uncommon Disorder Of The Kidneys Characterized By A Normal Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis With Pr Renal Acidosis Metabolic Acidosis

Causes Of Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Intellectual Property Of Knowmedge Com Mnemonic Goldmark G O L D M Medical Mnemonics Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis

Pin By Donn Pierre On Pharm Mnemonics Steven Johnson Syndrome Steven Johnson

Elevated Anion Gap Metabolic Acidosis Abg Interpretation Lesson 8